When to Choose Die Casting and When to Select for Injection Molding
Author: SAIVS Date Published: May 05,2024
Die Casting and Injection molding are two prevalent manufacturing processes employed to create parts. While die casting utilizes molten metal to produce high-strength, precise metal components, injection molding is geared towards large-scale production of plastic parts using molten plastic. The selection between the two hinges on factors such as material requirements, part complexity, production volume, and cost considerations.
Die Casting Process:
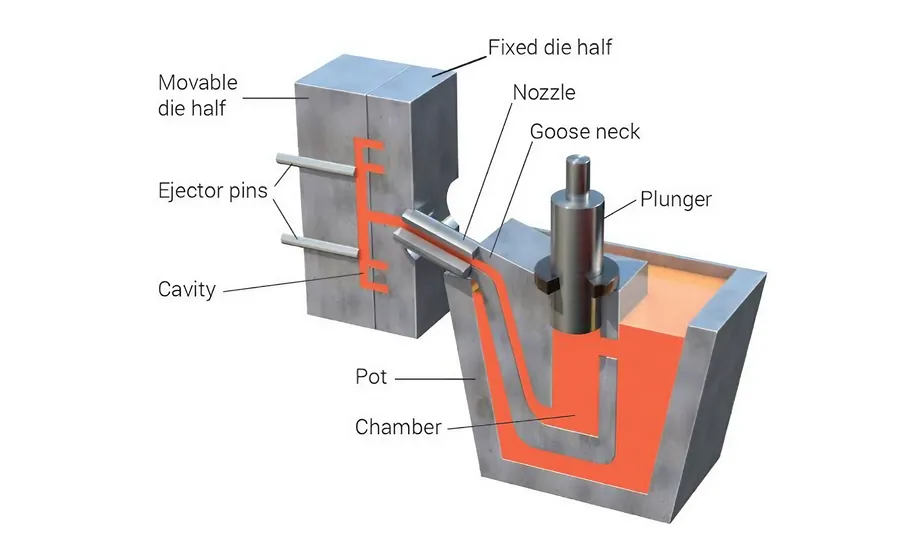
Step 1: Mold design & Making
The process begins with the creation of a mold designed by our engineers to suit the specific requirements of the die-cast part. Precision CNC Machining is commonly employed to craft the die-cast mold. The choice of mold material and the precision of its construction significantly influence the quality of the final die-cast parts.
Step 2: Mold Installation
Once the mold is prepared, it is installed onto dedicated casting equipment. The equipment parameters are meticulously adjusted to ensure the highest level of accuracy during the casting process for aluminum alloy parts.
Step 3: Material Preparation
Before casting begins, the die casting materials must be properly prepared to meet the specified requirements. Common die casting metals include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
Step 4: Injection
The metal ingots are melted, and the molten material is injected into the mold until it completely fills the mold cavity. Swift cooling follows, with precise control over cooling time and temperature crucial for ensuring the quality of the final cast parts.
Step 5: Demolding
Once the die-cast piece has cooled, it is removed from the mold, and any excess material is trimmed away to achieve net shape castings. Secondary operations, such as machining or surface treatments like powder coating, may be necessary to meet desired accuracy or surface finish requirements.
Step 6: Inspection & Packaging
To assess the quality of the die-cast part, thorough inspections are conducted, encompassing dimensional and surface quality checks. Upon passing inspection, the parts are carefully packaged to safeguard them from damage during transportation.
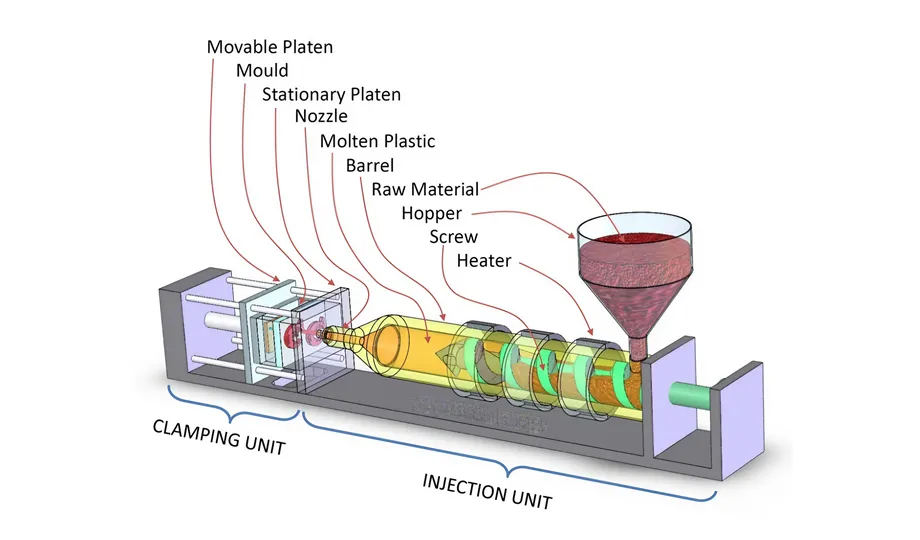
Injection Molding Process:
Step 1: Mold Design
The initial step in injection molding involves designing the mold. This process considers the part's design, dimensions, and other specifications to create a mold with an appropriate cavity shape for molding purposes.
Step 2: Material Selection & Melting
Plastic materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, ABS, or nylon are commonly used in injection molding. Material selection takes into account properties like strength, flexibility, and thermal stability. Once the material is chosen, it is fed into an injection molding machine, where it is heated and melted.
Step 3: Injection
Molten plastic is injected under high pressure into the mold, filling every corner of the mold cavity to form the desired shape.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After filling the mold cavity, the plastic material cools and solidifies to its final state. Proper cooling procedures are essential to prevent defects like warping or sink marks.
Step 5: Mold Opening and Ejection
Once the plastic material solidifies in the mold, the solid injection molded plastic parts are formed. Ejector pins in the mold assist in pushing the parts out.
Step 6: Post-Processing
After ejection, the parts may undergo further processing, such as trimming, polishing, or painting, to enhance their aesthetic or functional properties.
Step 7: Quality Inspection
Finally, the finished parts undergo quality assurance inspections to verify dimensions, structural integrity, and appearance, ensuring they meet specified specifications.
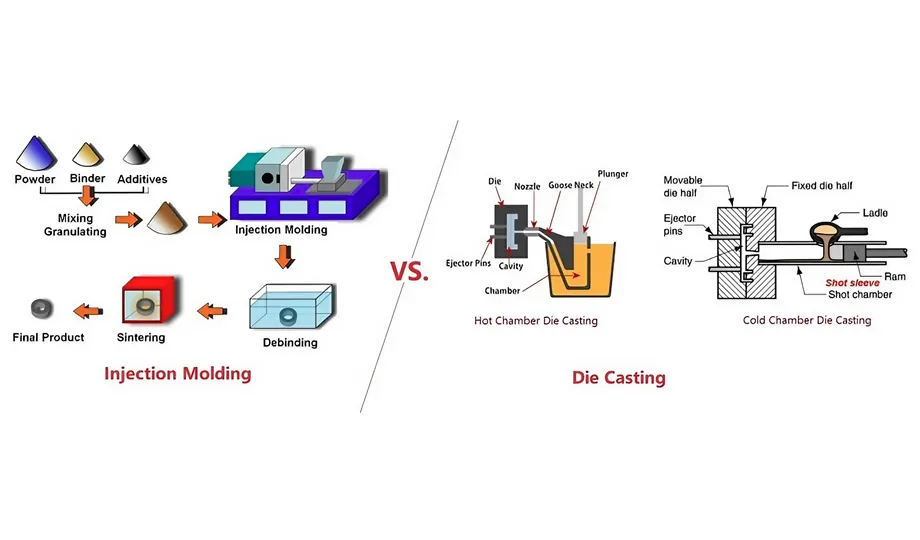
Comparing Die Casting and Injection Molding: Key Differentiators
The choice between die casting and injection molding hinges on several key differentiators, including the type of material used, the desired level of precision and tolerances, mold costs, production speed, surface finish requirements, and suitability for specific applications.
Material: Die casting is restricted to non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, while injection molding offers a broader range of options, encompassing a wide variety of thermoplastics.
Precision and Tolerances: Die-cast parts generally exhibit higher precision and tighter tolerances compared to injection-molded components.
Mold Cost: Die casting molds typically involve a higher initial investment compared to injection molding molds.
Production Speed: Both die casting and injection molding can achieve fast production rates, catering to high-volume manufacturing needs.
Surface Finish: Die-cast parts often possess a smooth surface finish, while injection-molded components may require additional post-processing to achieve the desired finish.
Application Suitability: Die casting is ideal for producing complex shapes and high-strength parts, while injection molding excels in manufacturing large parts and a diverse range of materials.
Selecting the Right Process: Considerations for Your Project
The optimal choice between die casting and injection molding depends on the specific requirements of your project. If your project demands parts that are strong, precise, and exhibit a smooth surface finish, die casting may be the preferred option. However, if the project involves large-scale production of parts using a wide range of materials, injection molding might be a more suitable choice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the typical applications of die casting?
Die casting is commonly employed in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries to produce components such as engine blocks, transmission housings, and electronic enclosures.
Q2: What are some common injection-molded products?
Injection molding is widely used to manufacture a vast array of products, including bottles, containers, toys, medical devices, and household appliances.
Q3: Which factors influence the cost of die casting and injection molding?
The cost of both processes is influenced by factors such as part complexity, mold design, material selection, production volume, and post-processing requirements.
Why Choose saivs?
SAIVS is a leading provider of die casting and injection molding services, offering a comprehensive range of manufacturing capabilities to meet the diverse needs of their customers. With over 20 years of experience in the industry, SAIVS has earned a reputation for quality, reliability, and customer service.If you are looking for a leading provider of die casting and injection molding services, please contact SAIVS today. They would be happy to discuss your needs and provide you with a quote.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Why is Stainless Steel Difficult to Machine
In this article, we will explore the main reasons why stainless steel is challenging to machine, including high cutting forces and temperatures and accelerated ...
-

Comparison of Silica Sol and Water Glass in Precision Casting
This article will explore the characteristics, applications, and advantages of Silica Sol and Water Glass, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role...
-

Sequence of Investment Casting Technology
Each mode of production has its own production sequence. Actual operators must produce in accordance with their production sequence, rather than in disorder, wh...
-
Forging and stamping: the current status of automobile stamping technology
The modern automotive industry demands ever-increasing production scale, multi-model compatibility, and large, integrated body panels. Traditional rigid, s
-

Brief Talk about Common Defects in Castings and Causes
Pore defects in castingsWhen a molten metal solidifies, there is no time for gas to escape and form round holes in the metal surface or interior. There are thre...
-

Repairing Defects in Investment Castings
From the defect causes to repair methods, a comprehensive analysis of investment casting defects repair knowledge, help you to understand the casting process.