Sandblasting vs. Abrasive Blasting: Understanding the Nuances
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Jul 08,2024
Sandblasting and Abrasive Blasting are both essential techniques in Surface Preparation, often used to clean, smooth, or shape material by propelling Abrasive Media under high pressure. Although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are key differences between the two methods. Understanding these differences can help professionals select the appropriate technique for their specific application, ensuring optimal results and efficiency.
Sandblasting
As the name suggests, sandblasting traditionally uses sand as the primary abrasive material. This method has been popular for many years, particularly for its effectiveness in removing rust, paint, and other contaminants from surfaces. The process involves projecting a stream of fine sand particles at high velocity onto a surface. The abrasive action of the sand particles removes the top layer of the material, revealing a clean and smooth surface underneath.
However, sandblasting has some significant drawbacks. Using sand generates a considerable amount of dust, which can pose serious health risks if inhaled, such as silicosis, a lung disease caused by inhaling fine silica particles. Consequently, the use of sand in blasting operations has been restricted or banned in many regions due to health and environmental concerns.
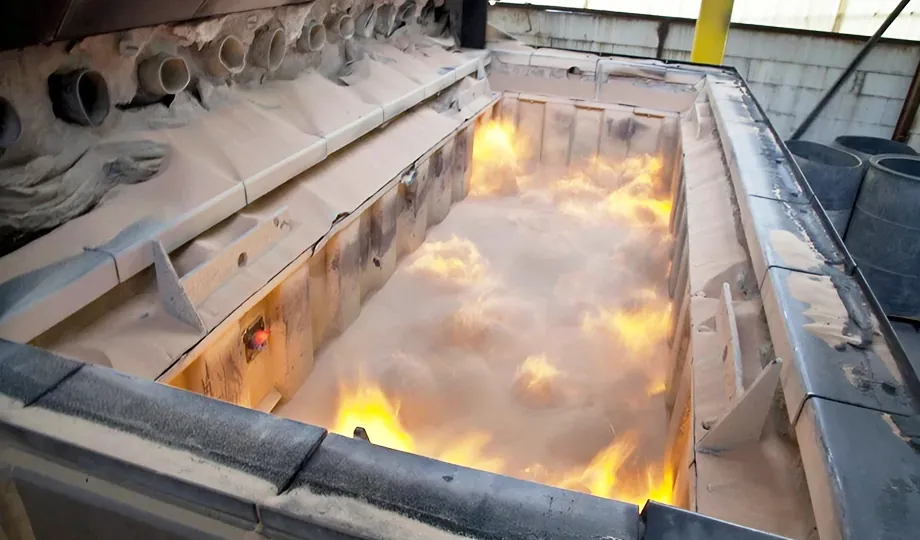

Abrasive Blasting
Abrasive blasting is a broader term that encompasses various blasting techniques using different types of abrasive media. Unlike sandblasting, abrasive blasting can employ a wide range of materials, including glass beads, steel grit, Aluminum oxide, and plastic media, among others. This versatility allows abrasive blasting to be tailored to specific applications, offering advantages in terms of efficiency, safety, and surface finish.
One of the significant benefits of abrasive blasting is the ability to select media that minimize health risks and environmental impact. For example, using materials like glass beads or plastic media generates less dust and can be safer for operators. Additionally, different media can produce varying surface textures and finishes, making abrasive blasting suitable for delicate surfaces and precise applications.
Common types of bead blasting media
Glass beads: The most popular type of bead blasting media, glass beads are generally used for cleaning and finishing delicate surfaces. They are available in various sizes, from very fine to quite coarse. Finer glass beads are used for polishing, while coarser beads are used for cleaning and deburring.
Glass bead blasting media
Ceramic beads: Similar to glass beads, ceramic beads are a good choice for cleaning and finishing delicate surfaces. They are also very durable and can be reused many times.
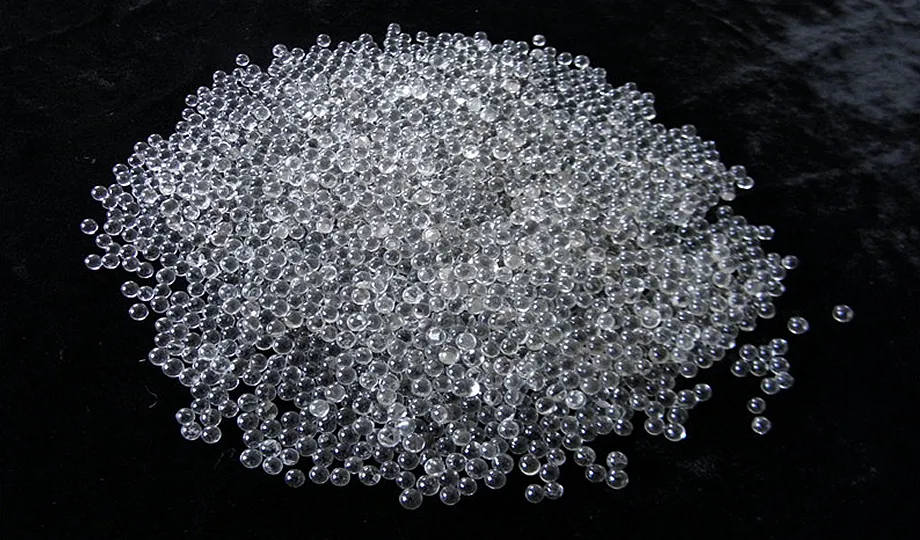

Ceramic bead blasting media
Plastic beads: Less aggressive than glass or ceramic beads, plastic beads are often used for cleaning soft materials such as plastics and composites. They are also a good choice for deburring sharp edges.
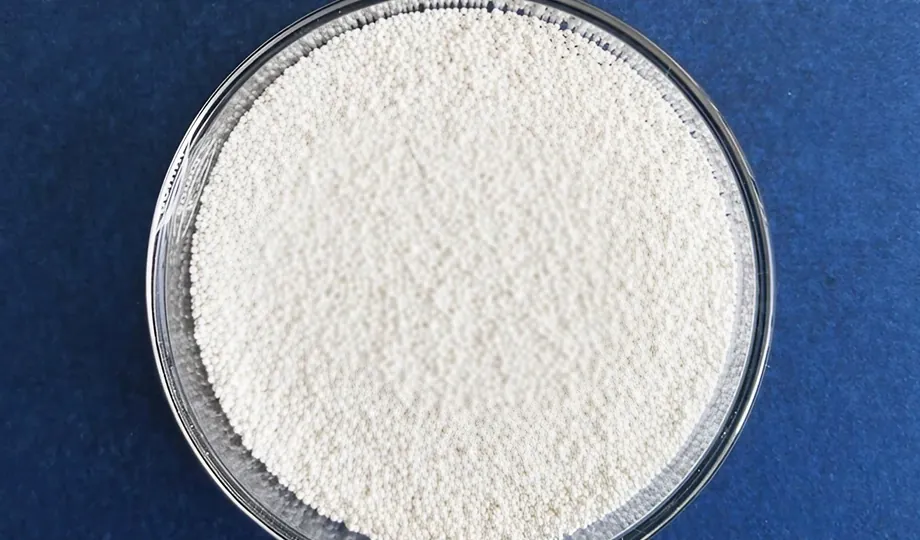

Plastic bead blasting media
Walnut shells: A natural and biodegradable media, walnut shells are a good choice for cleaning and finishing wood and other soft materials. They are also a good option for removing rust from delicate surfaces.
Walnut shell bead blasting media
Aluminum oxide: A very aggressive media, aluminum oxide is used for heavy-duty cleaning and deburring. It is not recommended for use on delicate surfaces.
Key Differences
The primary difference between sandblasting and abrasive blasting lies in the choice of abrasive media. Sandblasting specifically uses sand, while abrasive blasting can use a variety of materials. This distinction impacts several aspects of the blasting process:
1. Health and Safety: Sandblasting generates more hazardous dust compared to many alternative abrasive media. Regulations often favor abrasive blasting with safer media.
2. Versatility: Abrasive blasting is more versatile, offering a range of media that can be matched to different materials and desired finishes.
3. Environmental Impact: Abrasive blasting can be more environmentally friendly, especially when using recyclable and less hazardous media.
4. Surface Finish: Different media in abrasive blasting can achieve specific textures and finishes, catering to diverse industrial needs.
In conclusion, while sandblasting and abrasive blasting serve similar purposes in surface preparation, the latter provides greater flexibility, safety, and efficiency due to the variety of media available. Understanding these differences helps professionals make informed decisions, ensuring the best outcomes for their projects.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-
Investment Casting: Unveiling the Magic of Wax Patterns
This guide delves into the various types of investment casting waxes, their unique properties, and how they contribute to the success of this versatile techniqu...
-

Network Burrs in Aluminum Alloy Die Casting
Learn how optimizing die design, controlling temperatures, adjusting fill speeds, and improving cooling systems can enhance casting quality and production effic...
-

Aluminium Casting Vs. Steel Casting: Which Alloy Is Right For Your Product
Introducing Green Sand CastingCasting products are used in a variety of industries, making casting an important manufacturing process. Many of these products ar...
-

Investment casting: a comparison between stainless steel and aluminum
Investment casting is a widely used manufacturing process that allows the production of complex and intricate metal components with high dimensional accuracy. W...
-

Quenching, Tempering, Annealing, Normalizing: The Essential Heat Treatment Techniques for Steel
Heat treatment is a crucial process in metallurgy for primary processes that stand out: quenching, tempering, annealing, and normalizing.
-

Why Choose Haworth Castings For Your Cast SAIVS?
SAIVS Castings specializes in producing high-quality cast enclosures for various industrial sectors. Enclosures are protective housings that provide a secure ba...

