Rapid Injection Molding: A Guide to Fast-Track Production
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Apr 28,2024
Rapid Injection molding is a variation of injection molding designed for the rapid production of plastic parts in small to medium volumes. It bridges the gap between initial prototypes and mass production, offering a cost-effective solution for projects requiring fast turnaround times.
What is rapid injection molding?
Traditional injection molding excels in high-volume production but involves lengthy lead times due to the complexity and expense of tooling. RIM addresses this challenge using simpler, faster-to-manufacture molds often made from aluminum or soft steel. While these molds may not match the durability of hardened steel molds used in traditional injection molding, they enable significantly faster production of parts for prototyping, low-volume manufacturing, or bridge tooling needs.
How Does Rapid Injection Molding Work?
The core principles of rapid injection molding are similar to traditional injection molding:
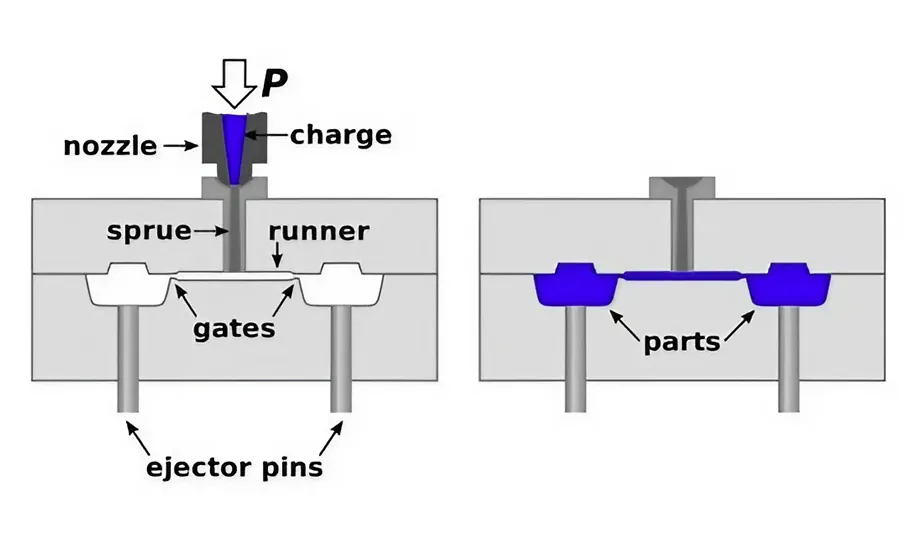
Design and Prototyping: The process begins with the creation of a detailed design using CAD software. Factors like wall thickness, surface finish, and material selection are crucial for achieving a high-quality final product. 3D Printing may be used to generate a physical prototype for evaluation and testing.
Mold Making: Once the design is finalized, mold creation commences. Aluminum molds are popular due to their affordability and rapid turnaround times compared to traditional steel molds. CNC machining and electrical discharge machining (EDM) are commonly used techniques for crafting these molds with high accuracy.
Material Selection: Selecting the appropriate resin material is vital for the project's success. The part's end-use application, mechanical properties, and aesthetic requirements all play a role in material selection. Engineering resins, ABS, polypropylene, and polycarbonate are frequently chosen for their durability and performance.
Injection Molding Process: The chosen material is melted and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure using an injection molding machine. This stage is meticulously monitored to ensure optimal molding conditions and achieve the desired quality.
Cooling and Ejection: The part cools and solidifies within the mold after injection. Cooling channels within the mold help regulate the cooling rate for even solidification. Once cooled, the part is ejected from the mold, signifying the completion of the molding cycle.
Post-Processing: Depending on the part design and application, post-processing steps such as drilling, painting, or assembly might be necessary to refine the part's appearance, enhance its properties, or prepare it for its final use.
Quality Assurance: Each part undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets the specified requirements and quality standards. Measurements and tests are conducted to assess the part's dimensions, material properties, and overall integrity.
Advantages of Rapid Injection Molding
Material Versatility: RIM offers remarkable flexibility in material selection. Unlike 3D printing, where material changes necessitate significant alterations, RIM readily accommodates a wide range of thermoplastics, elastomers, and composites without major system modifications. This adaptability makes RIM suitable for diverse industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical applications.
High-Quality Parts: RIM prioritizes cutting-edge design for manufacturability principles to ensure parts meet rigorous quality standards. High-pressure injection of molten resin guarantees uniform wall thickness and optimal ejection angles, resulting in a robust final product with minimal porosity. This surpasses 3D printing processes that may introduce unsintered areas, compromising part strength.
Disadvantages of Rapid Injection Molding
High Initial Costs: A primary drawback of RIM is the high upfront investment associated with specialized tooling. Mold development costs can range from $2,000 to several thousand dollars, depending on complexity and size. This initial investment necessitates careful consideration, especially for low-volume production runs.
Extended Lead Times: RIM has longer lead times compared to CNC machining and 3D printing. Designing and manufacturing complex molds can take 5-7 weeks and 2-4 weeks, respectively. Cooling and runner systems within the mold further contribute to lead times. Design modifications can further extend production timelines. Partnering with a manufacturing expert can help streamline the design, testing, and production processes.
Equipment Used in Rapid Injection Molding
Injection Molding Machines: These machines form the core of the process, melting and injecting the plastic material into molds under high pressure.
CNC machining centers: Used for creating the molds with the required precision to meet specific part tolerances and geometries.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Equipment: Useful for crafting intricate details in complex molds.
3D Printing Devices: Often employed in the prototyping stage to produce mold prototypes or parts directly from CAD data, accelerating design verification.
Aluminum and Steel for Molds: Material selection is crucial, with aluminum being a popular choice for rapid prototyping due to its affordability and faster turnaround times.
Plastic Resin Dryers: Drying plastic resins before injection is essential to prevent quality issues in the final product.
Temperature Controllers and Chillers: Regulate the temperature of the mold and the plastic material for optimal production conditions.
Part Removal Robots and Automation Equipment: In some setups, robots are used to enhance efficiency and consistency by removing finished parts and performing secondary operations.
Differentiating Rapid Injection Molds from Standard Injection Molds
The key differences between molds used in RIM and traditional injection molding lie in their material composition, design complexity, lifespan, and cost:
Material: RIM molds are typically crafted from aluminum or other materials that are easier and faster to machine compared to the tool steels used in standard injection molding. This significantly reduces mold production lead times.

FAQs
Q: What is the typical production cycle time for rapid injection molding?
A: The production cycle for rapid injection molding usually depends on the size, complexity, and quantity of parts required, but can usually be anywhere from a few days to a few weeks.
Q: What are some common plastic materials used in rapid injection molding?
A: Commonly used plastic materials include polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), polycarbonate (PC), nylon (PA), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Material selection requires consideration of part requirements and the application environment.
Q: What are the limitations of rapid injection molding?
A: Limitations of rapid injection molding include limited size and number of parts to be manufactured, limited selection of some materials, and costs that may be higher for mass production. In addition, the manufacture of complex parts may require more process optimization and debugging to ensure the quality and accuracy of the final product.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Shaft Components: The Best Choice For CNC Machining
From solid to hollow, delve into CNC machining precision, uncovering routes from turning to drilling.
-

Die Casting Design Guide
AbstractDie casting, a high-pressure metal casting process is widely used in manufacturing industries for producing complex metal parts. This article delve
-

Unveiling The Secrets Of Stainless Steel Gearboxes
About the definition, advantages, and maintenance of steel gearbox products.
-

Understanding Surface Roughness in CNC Machining
Learn about its importance, measurement, and impact on CNC machined parts, and explore various surface finishes and their applications.
-

From Wax to Metal: Unveiling the Art of Lost Wax Casting
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of lost wax casting, including its applications, suitable metals, wax types, and its relationship with invest...
-

Control method of air hole defect and external shrinkage of aluminum castings
1、 Causes and control methods of air hole defects in aluminum castingsDuring aluminum alloy die casting, the liquid metal contains a lot of gas. If the melting ...

