Powder Coating: A Durable and Sustainable Finishing Solution
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Jun 17,2024
Powder coatings are dry finishing systems offering superior performance and aesthetics compared to traditional liquid coatings. They are widely used across various industries due to their durability, environmental benefits, and versatility.

Application of Powder Coatings
Powder coating is applied as a dry powder and cured under heat, forming a hard finish suitable for plastic, glass, or metal surfaces. The process involves:
Preparation: Crucial for adhesion, involving sandblasting and priming the surface.
Application: Powder is applied using an electrostatic gun or fluidized-bed application. The powder is charged and sprayed onto the surface using compressed air.
Curing: The coated surface is heated to allow the powder to melt and form a film. Once cooled, the coating hardens.
Types of Powder Coatings
Thermoplastic: Becomes softer and more liquid when heated, making it reusable. Suitable for refrigerators, Auto Parts, and metal fencing.
Thermoset: Forms chemical bonds when cured, non-recyclable but ideal for high heat areas. Often cheaper than thermoplastics.
UV Curable Powder Coating: An advanced technique using UV light for curing.
Composition of Powder Coatings
Powder coatings are dry mixtures that provide a durable, high-quality finish. They contain four main components: binders, additives, pigments and dyes, and fillers.
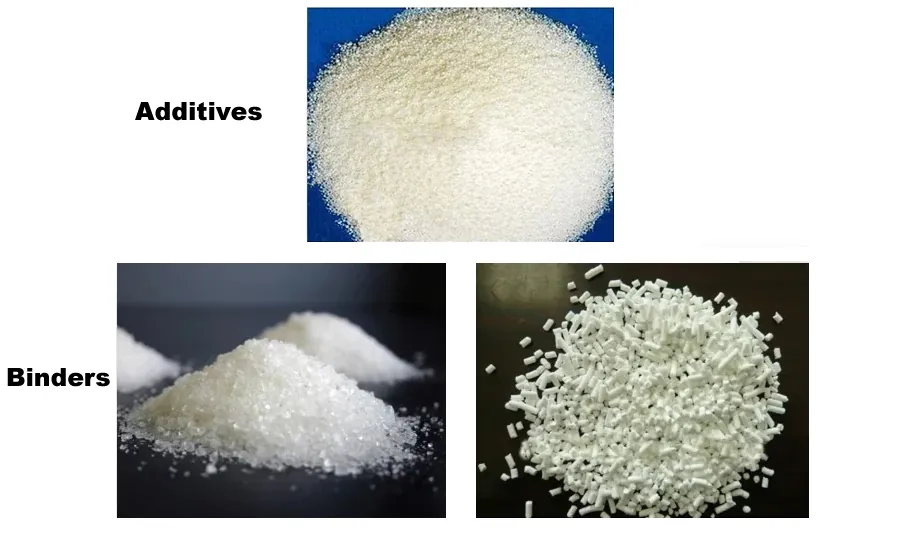
Binders
Binders form the foundational structure and performance of powder coatings, typically composed of resin and hardener. Common resin chemistries include:
Polyester: Offers excellent exterior durability, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and architectural elements.
Epoxy: Provides outstanding mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, suitable for industrial and automotive applications.
Polyurethane: Known for its smooth and glossy finish, often used in high-quality automotive coatings and wood finishes.
Epoxy-Polyester (Hybrid): Combines the strengths of epoxy and polyester resins, versatile for various applications.
Acrylic: Excellent for color and gloss retention and decorative and architectural applications.
Additives
Additives enhance specific characteristics and performance of powder coatings. Categories include:
Appearance (Flow Control) Additives: Prevent issues like cratering or orange peel, ensuring a smooth finish.
Degassing Additives: Help release air from the film while maintaining its open structure.
Exterior Durability Additives: Protect the coating from sunlight and environmental factors, often including UV absorbers.
Corrosion Resistance Additives: Zinc dust additives provide extra protection against corrosion.
Charge Control Additives: Enhance the coating’s ability to accept an electric charge during application.
Gloss Control Additives: Used to achieve the desired level of gloss, involving both chemical and physical methods.

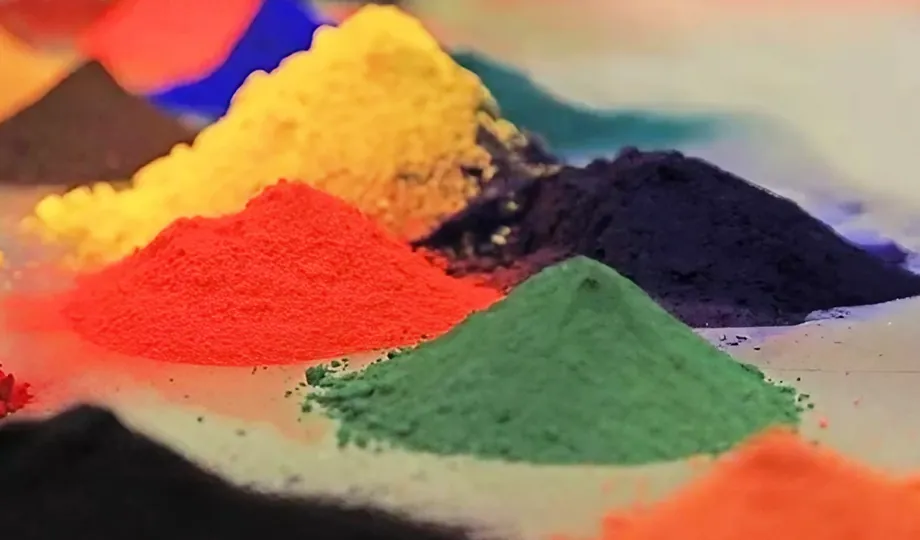
Pigments and Dyes
Pigments provide color and aesthetic appeal, available as organic or inorganic types. They must withstand curing temperatures and exposure conditions. They offer:
Hiding Power: Effectively concealing the substrate's color or imperfections.
Appearance: Creating the desired look and finish, from high gloss to matte.
Fillers
Fillers add volume and ensure optimum packing density. Common fillers include natural minerals like calcium carbonate.

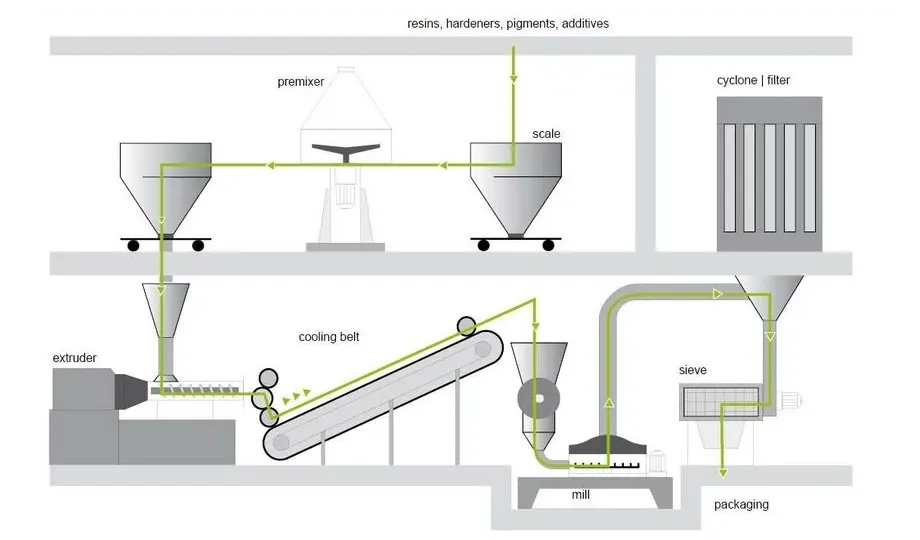
Manufacturing Process of Powder Coatings
The production of powder coatings involves several precise steps to ensure quality and consistency:
Formula Development: Custom recipes are created based on specific customer requirements and usage needs.
Weighing: Ingredients are accurately weighed into a container.
Mixing: Raw materials are mixed horizontally and vertically using a special machine at defined speeds and times.
Extrusion: The mixture is melted in an extruder to create a homogeneous mass through heat and shearing forces.
Cooling: The melted mass is cooled on a belt, rolled out, and broken into small chips by a shredder.
Grinding: Hardened, cooled extrudate is first broken into rough chips and then ground into fine powder.
Sieving: Coarse particles and fine parts are filtered out using sieves and suction.
Filling: The finished powder coating is packaged in airtight containers.
Conclusion
Powder coating offers a compelling alternative to traditional liquid coatings, providing superior performance, aesthetics, and environmental benefits. Its versatility allows application across various industries, from automotive and construction to household appliances and furniture. The controlled application process ensures a durable, high-quality finish with excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and UV rays. With advancements in technology, powder coating continues to evolve, offering even more efficient and sustainable solutions for surface finishing needs.
FAQS
Q:How Long Does Powder Coating Take?
A:The powder coating process typically takes a few hours, including preparation, application, and curing. Surface Preparation can take from a few minutes to several hours, the application usually takes 15-30 minutes, and curing generally requires 10-20 minutes at 350°F to 450°F (177°C to 232°C), depending on the specific powder formulation and oven temperature.
Q:How Much Does Powder Coating Cost?
A:The cost of powder coating varies widely depending on the size and complexity of the item, with small items like bicycle frames costing $50 to $150, medium items like metal furniture ranging from $100 to $300, and large items such as industrial equipment starting at $300. Commercial rates for large batches or continuous production typically range from $3 to $10 per square foot.
Q:How Thick Is Powder Coating?
A:Powder coating thickness typically ranges from 2 to 6 mils (50 to 150 microns), but can vary based on application requirements. Thin coatings can be as low as 1 mil (25 microns) for precision applications, while thick coatings can reach up to 10 mils (250 microns) for enhanced protection in heavy-duty environments.
Q:Advantages and Disadvantages of Powder Coating
A:Powder coating offers several advantages, including durability, environmental friendliness due to negligible VOC emissions, efficiency with minimal waste, a uniform finish, and a wide range of color options. However, it also has disadvantages such as high initial setup costs, difficulty in coating complex shapes, the necessity of curing which limits item size, labor-intensive surface preparation, and challenges in achieving extremely thin or thick coatings.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Aluminum Vs Magnesium:How To Select For Gravity Die Casting?
Aluminum gravity die casting is a process in which molten aluminum is poured into a mold under the force of gravity.The process is relatively simple and inexpen...
-

How CNC Machining Is Changing the Medical Industry
Digital motors, sophisticated software, and specialized cutting tools are yielding precision, repeatability, and scalability in CNC machining.Products, devices,...
-

Influence of Metal Forging Process on Part Quality
Through the analysis of forging defects, this paper puts forward suggestions for optimising the forging process, aiming to improve the quality of forgings.
-

The significance of gearbox in industrial applications
Gear systems are integral to a wide range of industrial applications, from automotive to manufacturing machinery. Within these systems, the gear housing...
-

Roughing and finishing in CNC machining
Roughing and finishing are two key steps in machining that play different but equally important roles.Definition and Role of Roughing: The main purpose of
-

Understanding 3D Printing Technologies and Inspection Methods
This article explores seven main categories of 3D printing and the inspection methods used to guarantee the quality and reliability of printed parts.

