Safeguarding Product Reliability: Penetrant Testing and Ultrasonic Flaw Detection for Castings
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Feb 26,2024
Casting Defects pose challenges in various industries, and accurate inspection methods are crucial to ensuring the quality and reliability of cast products.
Two widely employed non-destructive testing (NDT) methods for this purpose are penetrant testing (PT) and ultrasonic flaw detection.

Penetrant Testing (PT):
Penetrant testing is a non-destructive method that utilizes the permeability and capillary action of colored or fluorescent penetrants to identify surface defects.
It involves applying penetrant, removing excess penetrant, and using imaging treatment to enhance and display defects.
While effective for surface flaws, PT cannot accurately represent the nature, shape, size, or depth of discontinuous defects.
Critical Factors for Penetrant Testing:
Quality and Proportion of Penetrant: The effectiveness of the inspection relies on the penetrant having excellent wetting properties for proper penetration.
Colored and Fluorescent Methods: Colored dyes and fluorescent powder are used for display,
with the latter requiring a darkroom environment for fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
Procedure for Penetrant Testing:
Surface Preparation: Prior to inspection, thorough cleaning of castings is essential to remove contaminants like rust, scale, paint, and grease.
Inspection: After applying penetrant and imaging treatment, defects are visually identified.
Post-Inspection: Removal of penetrant and developer is followed by necessary drying and corrosion protection.
Characteristics and Scope of Penetrant Testing:
Simple and adaptable method and equipment.
Not limited by casting shape, but surface roughness affects quality level.
High sensitivity, simple operation, and not restricted by material properties.
Limited to detecting surface or near-surface defects, requiring additional methods for internal defect detection.

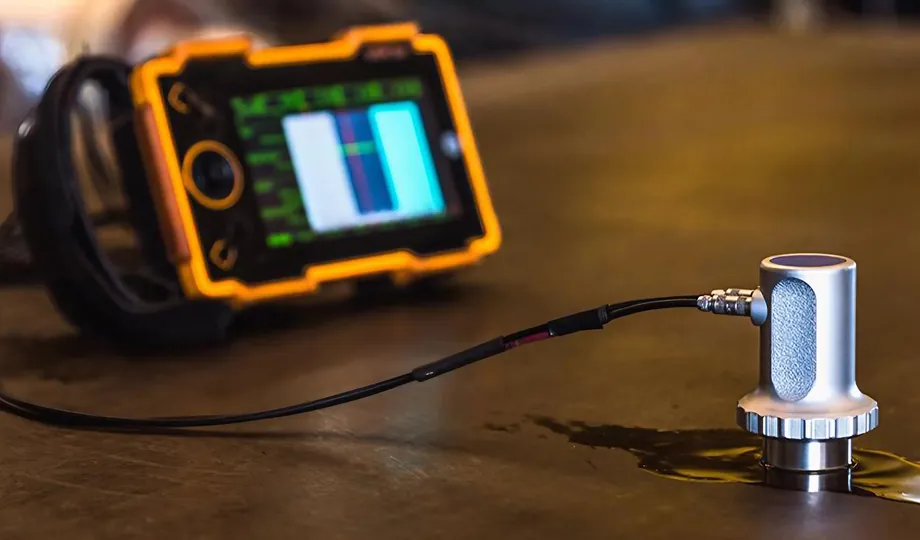
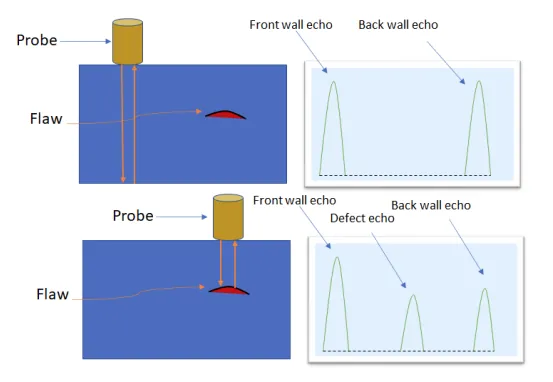
Ultrasonic Flaw Detection:
Ultrasonic testing involves injecting high-frequency ultrasound into castings and detecting internal defects based on
refraction and waveform transformation characteristics. Three types of ultrasonic testing include pulse reflection,
penetration, and resonance methods, with the pulse reflection method being commonly used.
In Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
Higher frequency sound waves (beyond human hearing) are generated from a transducer on the test material.
Ultrasonic waves can detect faults, defects, cracking, inclusions, and impurities by evaluating the front wall echo, rear wall echo, and defect echo.
Crystalline piezoelectric materials, such as quartz, are used to build transducers. When electricity is applied, these materials vibrate to produce ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasonic echoes move freely in any direction, and interference with their reception in the transducer allows for the detection of internal flaws.
Ultrasonic echoes pass through the material and are returned to the transducer, providing information about the material's internal condition.
In summary, addressing manufacturing flaws involves understanding and mitigating factors such as material quality, Mold design,
and solidification processes, and employing effective NDT methods like ultrasonic testing for comprehensive defect detection.
Sensitivity: Influenced by factors such as ultrasonic wave frequency, flaw detector magnification, and transmission power.
Coupling Method: Smooth transmission requires appropriate coupling methods like water, lubricating oil, or transformer oil.
Features of Ultrasonic Flaw Detection:
High detection sensitivity, capable of detecting low-pressure defect signals.
Precise defect location accuracy and resolution.
Wide applicability, except for certain materials like austenitic Steel Castings.
Cost-effective, high-speed, and capable of detecting large thicknesses.
The occurrence of manufacturing flaws in metal cast products can be attributed to various factors related to the raw materials,
mold cavity design, component geometry, melting and pouring procedures, and solidification processes.
These flaws can be broadly categorized into three primary types: mini or micro defects, inclusion of foreign materials, and line defects.
Mini or Micro Defects:
Porosity and Micro Porosity: Small holes in the metal, with porosity being holes smaller than 1.5mm in diameter.
Gas Holes: Larger holes caused by gases expelled during solidification, often acting as barriers during pouring.
Inclusion of Foreign Materials:
Sand, Slag, and Impurities: The presence of non-metallic particles such as sand and slag, as well as impurities in the environment,
can lead to defects like cold closes due to a lack of fusion.
Line Defects:
Hot Tears: Sharp, abrasive cracks caused by pressures during solidification when metal contracts and is constrained at the mold's wall.
Shrinkage Fractures: Form when the volume of liquid metal reduces to a solid piece during solidification in the absence of necessary molten metal.
To address these flaws, various Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods are employed, including penetrant testing and ultrasonic testing.
While radiography has harmful impacts on human cells, ultrasonic testing is considered the most effective and safe approach.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

The common production problem and analysis of die casting moulds
Expanding on the Provided Information and Incorporating Additional InsightsCommon Die Casting Mould Production Problems and AnalysisMolten Metal Splash (Ru
-

Guide to Choosing Corrosion-Resistant Metals for Industrial Use
Understanding Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Essential Knowledge for Reliable, Long-Lasting ComponentsIn various industrial applications, corrosion-resista
-

Powder Coating: A Durable and Sustainable Finishing Solution
Powder coating offers a superior alternative to traditional liquid coatings. Learn about the process, composition, and FAQs about powder coating.
-

Investment Casting: Why Are Opening Costs So Low
Investment Casting is a widely used casting process for manufacturing complex-shaped parts, favored for its excellent surface finish and precise dimensiona
-
CNC Machining Tolerance Guidelines
IntroductionCNC machining is a precise manufacturing process that involves the use of computer-controlledmachines to create intricate parts and components. One ...
-

Shaft Components: The Best Choice For CNC Machining
From solid to hollow, delve into CNC machining precision, uncovering routes from turning to drilling.

