From Iron Alloys to Aluminum Alloys: Understanding the World of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Apr 15,2024
metals are broadly classified into two categories: ferrous and non-ferrous metals. This distinction is primarily based on the iron content of the metal. Ferrous metals, as the name suggests, contain iron as their major constituent, while non-ferrous metals do not. This fundamental difference in composition leads to a variety of contrasting properties and applications for these two groups of metals.
I. What are Ferrous Metals?
Ferrous metals are predominantly composed of iron, with a minimum iron content of 50%. They are characterized by their high strength, durability, and relatively low cost, making them essential materials in construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure. The most common ferrous metals include:
Iron: Pure iron is relatively soft and malleable, but when combined with carbon in varying amounts, it forms steel and Cast Iron.
Steel: Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, with carbon content ranging from 0.05% to 2.14%. It is the most widely used ferrous metal due to its exceptional strength, versatility, and ability to be further enhanced through alloying with other elements.
Cast Iron: Cast iron contains a higher carbon content (2% to 4%) compared to steel, along with silicon and manganese. It is known for its excellent compressive strength, making it suitable for applications like engine blocks and pipes.
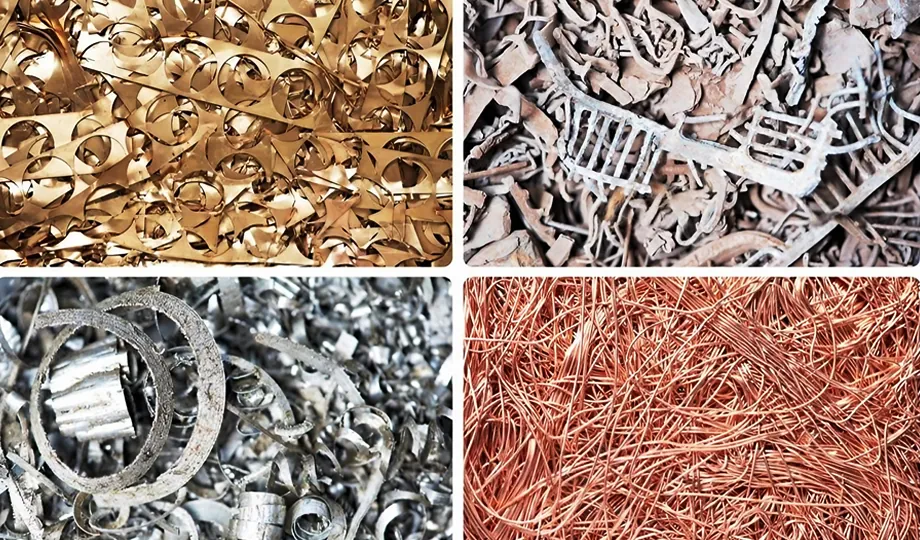

II. What are Non-ferrous Metals?
Non-ferrous metals are all metals that do not contain iron as their primary component. They encompass a diverse range of elements with unique properties and applications. Some of the most common non-ferrous metals include:
Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal with high electrical conductivity. It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and packaging industries.
Copper: Copper is a highly conductive and ductile metal, making it ideal for electrical wiring, plumbing, and cookware.
Gold: Gold is a precious metal valued for its luster, malleability, and resistance to tarnishing. It is used in jewelry, electronics, and as a monetary reserve.
Silver: Silver is a precious metal with excellent electrical conductivity and a lustrous appearance. It is used in jewelry, coinage, and electrical components.
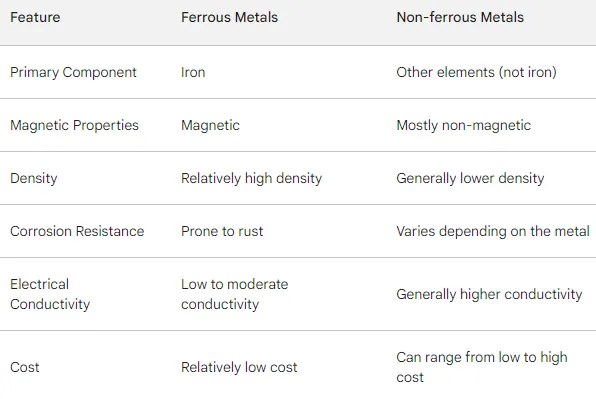
III. Distinguishing Ferrous from Non-ferrous Metals
IV. Common Ferrous Metals
Iron
Steel (various grades)
Cast iron
Wrought iron
V. Common Non-ferrous Metals
Copper
Lead
Zinc
Nickel
Tin
Gold
Silver
Platinum
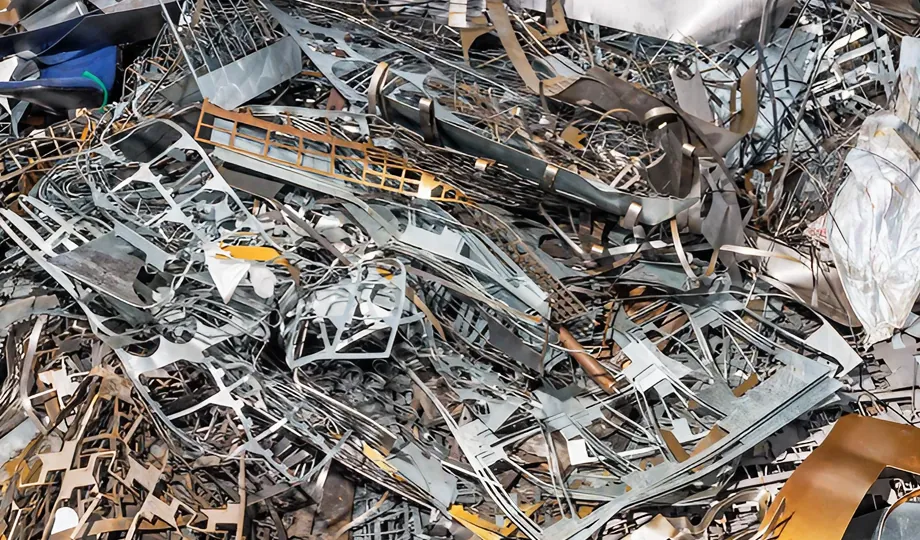

Ferrous and non-ferrous metals play crucial roles in various industries and applications. Their distinct properties make them suitable for a wide range of products and components. Understanding the characteristics and differences between these two metal groups is essential for making informed material selection decisions in engineering and design.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Unleashing the Power of Precision: CF8 Investment Casting for Superior Valve Bodies
Dive into the world of investment casting. Explore crafting valve bodies with CF8 stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance.
-

Unveiling the Indispensable Role of Molds in Aluminum Gravity Casting
Gravity casting is a commonly used casting process that utilizes the force of gravity to fill molds with molten metal, thus forming the desired castings. It is ...
-
6 Effective Strategies to Stop Rust in its Tracks
Learn how to prevent rust with smart choices & clever tricks. From steel secrets to coatings & care, keep your projects strong & beautiful. Start ru...
-

Achieving Precision: Mitigating Deformation in CNC Aluminum Machining
This guide explores aluminum properties, factors leading to deformation, and effective strategies to minimize it.
-

What is the process of gravity casting
What is Gravity Casting?Gravity casting, also known as gravity die casting or permanent mold casting, is a casting process used to produce high-quality metal pa...
-

Common problems during low pressure casting
Low-pressure casting is widely used in metal processing technology and plays a great role in China's modern industry. With the wide application of low-press...

