Forged vs Cast:Which Is Better
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Oct 23,2023
Metalworking processes play a crucial role in shaping various components and structures used in diverse industries.
Among these processes, Forging and casting are widely employed to transform raw materials into functional metal parts.
While both methods involve manipulating metals, they differ significantly in their approach and resulting characteristics.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Forging and Casting, explore their respective advantages,
and highlight the key differences between these two fundamental techniques.
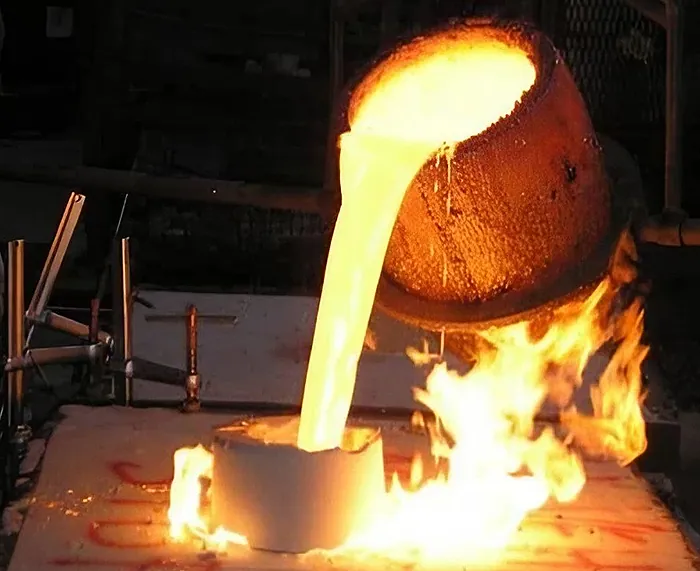

1. What is Forging?
Forging is a metalworking process that involves shaping heated metal through localized compressive forces.
It dates back thousands of years and has evolved with advancements in technology. During forging, a solid piece
of metal is subjected to high pressure using hammers or presses to reshape it into the desired form.
This method ensures superior strength by aligning the grain structure of the material along its shape.
2. What is Casting?
Casting, on the other hand, is a process that involves pouring molten metal into a mold cavity
to obtain a specific shape upon solidification. The molten metal can be derived from various sources
such as furnaces or induction heating systems. Once cooled and solidified within the mold, the metal
takes on its final form with intricate details faithfully replicated from the mold.
3. Advantages of Forging Metal:
Forging offers several distinct advantages when compared to other manufacturing methods:
a) Enhanced Strength: The compressive forces applied during forging refine grain structure alignment within metals,
resulting in improved mechanical properties such as increased strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance.
b) Superior Structural Integrity: As forged components maintain continuous grain flow without porosity or voids
that can weaken structural integrity, they exhibit exceptional reliability under demanding conditions.
c) Improved Material Utilization: Forging enables precise control over material deformation
while minimizing waste generation during production processes.
d) Customizability: With forging techniques like open-die or closed-die forging available for different applications,
manufacturers have flexibility in producing custom shapes according to specific requirements.
4. Advantages of Casting Metal:
Casting offers unique benefits that make it suitable for certain applications:
a) Complex Geometries: Casting allows for intricate designs with complex internal cavities or thin
sections that may be challenging to achieve through other manufacturing methods.
b) Cost-Effective for Large-scale Production: Mass production through casting can yield
significant cost savings due to reduced labor requirements and economies of scale.
c) Versatility in material selection: Castings can be produced from a wide range of materials including ferrous
alloys (e.g., steel), non-ferrous alloys (e.g., aluminum), as well as specialized alloys tailored for specific applications.
d) Replication Accuracy: Casting enables faithful replication of fine details from molds onto cast parts with minimal dimensional variations.
5. The Difference between Forging and Casting:
While both forging and casting share similarities as metalworking techniques aiming at
transforming raw materials into finished products, they differ fundamentally:
a) Process Approach: Forging involves shaping solid pieces by applying compressive forces whereas
casting employs molds filled with molten material that solidifies into desired shapes upon cooling.
b) Material Properties: Forged components possess superior mechanical properties due to refined grain structure
alignment achieved during deformation while castings exhibit variable properties depending on factors such as cooling rates.
c) Complexity vs Strength Trade-off: Castings excel at producing complex geometries but may
sacrifice some strength compared to forgings which prioritize structural integrity.
d) Cost Considerations: While forgings are often associated with higher upfront costs due to specialized
equipment requirements, castings offer cost-effective solutions for large-scale production runs.
Conclusion
Forging and casting are indispensable methods used extensively across industries for
transforming raw metals into functional components. Each technique has its own advantages based on specific
requirements related to strength demands or geometric complexities involved in component design.
Understanding these differences empowers manufacturers to select an appropriate method tailored precisely
towards achieving desired outcomes efficiently while maintaining optimal product performance standards.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-
Methods for Assessing 3D Printing Accuracy
Ensure your 3D prints meet specifications! Explore various methods for measuring dimensional accuracy, including 3D scanners, calipers, and micrometers.
-

Choosing the Right Material for Investment Casting
What is Investment casting?Investment casting is a metalworking process that involves creating a shape, called the investment, out of wax or other materials. Th...
-

Nickel-Based Alloy Casting: Superior Corrosion Resistance
What is Nickel-Based Alloy Casting?Nickel-based alloys are metallic materials that primarily consist of nickel,but they also include various other elements such...
-

What are the requirements of aluminum alloy die casting for the function of die steel?
1. High tempering resistance and cold and hot fatigue resistance of aluminum alloy die-castingMany aluminum alloy die-casting dies produced continuously should ...
-

How to Reduce Investment Casting Costs by 50%
Introduction:Investment casting, also known as precision or lost-wax casting, is a widely used manufacturing process with applications in various industries. Th...
-

Die Casting Design Guide
AbstractDie casting, a high-pressure metal casting process is widely used in manufacturing industries for producing complex metal parts. This article delve

