Die Casting Design Guide
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Aug 12,2024
Abstract
Die Casting, a high-pressure metal casting process is widely used in manufacturing industries for producing complex metal parts. This article delves into the critical aspects of die-casting design, from understanding the Design for Manufacturing (DFM) process to addressing potential surface treatment issues. It also covers key design factors such as wall thickness, parting lines, draft angles, ejector pins, fillets, radii, undercuts, and holes. By following these guidelines, engineers can design successful die-casting projects that meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Table of Contents
1.Introduction
2.The DFM Process in Die Casting
3.Potential Surface Treatment Issues in Die Casting Design
4.Key Design Factors for Die Casting Parts
5.How to Design a Successful Die Casting Project
6.Conclusion
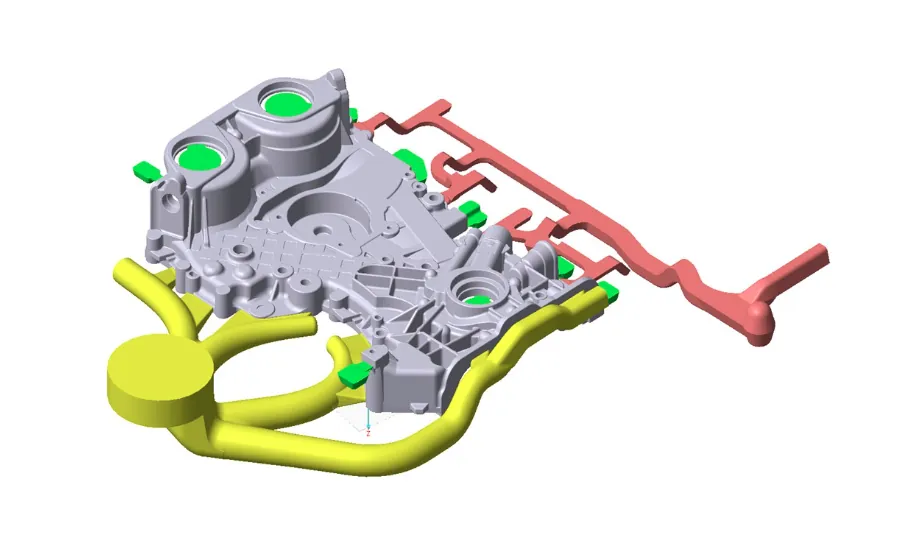
Introduction
Die casting is a versatile manufacturing process that involves injecting molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. This process is ideal for producing complex shapes with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish. However, successful die casting requires careful consideration of various design factors to ensure the production of high-quality parts.
The DFM Process in Die Casting
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a critical step in the die-casting process. It involves optimizing the part design to minimize production costs, improve part quality, and reduce lead time. The DFM process typically includes:
Design for Assembly (DFA): Ensuring that the part can be easily assembled into the final product.
Design for Cost: Identifying cost-saving opportunities through design changes.
Design for Testability: Incorporating features that allow for easy inspection and testing of the part.
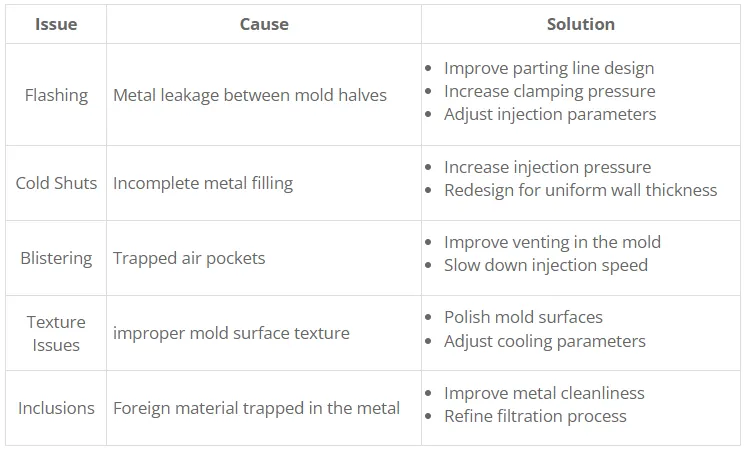
Potential Surface Treatment Issues in Die Casting Design
Die-casting parts may require additional surface treatments to improve their appearance, corrosion resistance, or other properties. Common surface treatment issues and considerations include:
Flash: Excess material that forms at the parting line.
Sink marks: Depressions in the surface caused by shrinkage of the molten metal.
Warping: Distortion of the part due to uneven cooling.
Key Design Factors for Die Casting Parts
Wall Thickness: Consistent wall thickness is crucial for uniform cooling and reduced warpage.
Parting Line: The parting line should be located in a non-critical area to minimize cosmetic defects.
Draft Angles: Sufficient draft angles allow for easy ejection of the part from the mold.
Ejector Pins: Proper placement of ejector pins ensures the part can be easily removed from the mold.
Fillets and Radii: Fillets and radii reduce stress concentrations and improve the appearance of the part.
Undercuts: Undercuts can complicate the Mold design and increase costs.
Holes & Windows: Holes and windows should be designed with sufficient web thickness to prevent breakage.
How to Design a Successful Die Casting Project
To design a successful die-casting project, follow these guidelines:
Involve the die caster early in the design process.
Use CAD software to create detailed 3D models.
Conduct a thorough design review to identify potential issues.
Consider the material properties and processing capabilities of the die-casting process.
Optimize the part design for manufacturability and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Die-casting design is a complex process that requires careful consideration of various factors. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, engineers can create designs that are both functional and manufacturable. By working closely with experienced die casters, manufacturers can achieve high-quality, cost-effective die-casting parts.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

How to Maximize the Efficiency of CNC Machining
CNC machining efficiency plays a crucial role in optimizing productivity and reducing costs. Here are some effective ways to improve CNC machining efficien
-

Choosing the Right Material for Investment Casting
What is Investment casting?Investment casting is a metalworking process that involves creating a shape, called the investment, out of wax or other materials. Th...
-

Design Considerations for Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is a widely used manufacturing process for producing complex, high-precision parts. Manufacturers achieve excellent dimensional accura
-

How to Reduce Aluminum Casting Costs
Discover how to reduce costs in aluminum casting with this comprehensive guide. Learn about design for manufacturability, alloy selection, process optimization,...
-

Process of CNC Rapid Prototyping
CNC Rapid Prototyping, also known as CNC-RP, is a process that combines computer numerical control (CNC) machiningwith rapid prototyping techniques to quickly p...
-

Unlocking Diversity: 3 Types of Sand Molds Commonly Used in Sand Casting
Learn about the 3 main sand molds used in sand casting.

