Cold Forging And Hot Forging:What Is The Difference
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Oct 26,2023
Forging is a widely used Manufacturing Process that involves shaping metal by applying compressive forces.
Two primary methods of forging are hot forging and Cold Forging, each with its unique characteristics and considerations.
Understanding the differences between these two techniques is crucial for manufacturers to make informed decisions
about which method to employ for their specific applications. In this article, we will explore the factors to
consider in both hot forging and cold forging processes, along with the advantages and disadvantages of each.
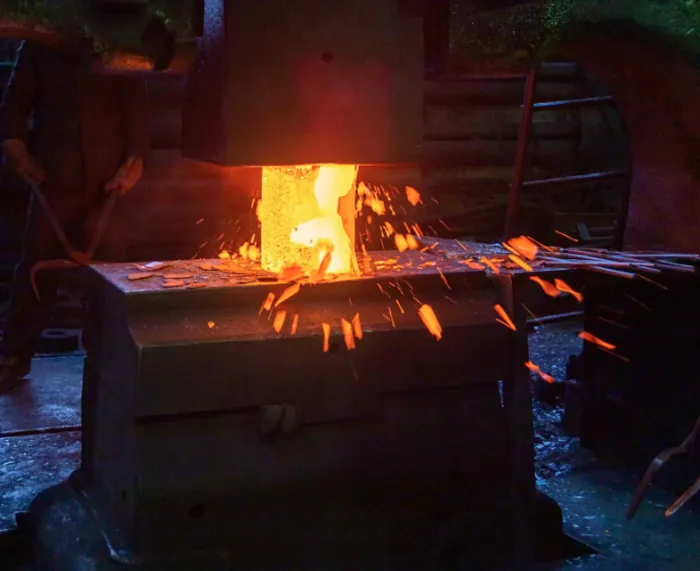

Factors to Consider in Hot Forging Process
Hot forging is a forging technique that involves deforming metal above its recrystallization temperature.
Here are some key factors to consider when utilizing hot forging:
1. Material Selection: Hot forging is suitable for a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and titanium.
However, the selection of materials should consider their ability to withstand the high temperatures involved in the process.
2. Temperature control: Maintaining precise and uniform temperatures is critical in hot forging.
Specialized heating equipment and controlled heating cycles are essential to achieve the desired material properties and forgeability.
3. Reduced Forming Forces: The elevated temperatures in hot forging reduce the required forming forces compared to cold forging.
This allows for greater deformation and shaping capabilities, making it suitable for complex and intricate designs.
4. Grain Structure and Mechanical Properties: Hot forging results in a refined grain structure and improved mechanical properties,
including enhanced ductility and reduced brittleness.
The recrystallization process during hot forging eliminates prior defects and improves material homogeneity.
Factors to Consider in Cold Forging Process
Cold forging, also known as cold working or cold forming, involves shaping metal below its recrystallization temperature.
Let's explore the factors to consider when employing cold forging:
1. Material Selection: Cold forging is typically used for softer metals such as copper, brass, and aluminum.
These materials exhibit better ductility and formability at lower temperatures.
2. Increased Forming Forces: Unlike hot forging, cold forging requires higher forming
forces due to the lower temperatures involved. This necessitates robust and powerful
forging equipment to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
3. Surface Finish and Precision: Cold forging offers excellent surface finish and dimensional precision,
making it ideal for producing intricate parts with tight tolerances. The absence of oxidation and scale
formation during the process contributes to superior aesthetics.
4. Work Hardening and Material Strength: Cold forging induces work hardening, resulting in increased material strength
and improved mechanical properties. The cold-worked metal exhibits higher tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hot Forging and Cold Forging
Advantages of Hot Forging:
- Enhanced material ductility and toughness.
- Greater formability for complex shapes.
- Improved material properties and grain structure.
- Lower forming forces compared to cold forging.
Disadvantages of Hot Forging:
- Limited to materials that can withstand high temperatures.
- Increased energy consumption and heating costs.
- Longer production cycles due to heating and cooling processes.
Advantages of Cold Forging:
- Superior surface finish and dimensional precision.
- High material strength and improved mechanical properties.
- Suitable for softer metals with better cold-forming characteristics.
- Reduced material waste and enhanced material utilization.
Disadvantages of Cold Forging:
- Higher forming forces required.
- Limited to simpler shapes and designs.
- Increased tool wear and maintenance costs.
- Lack of grain refinement and recrystallization benefits.
Conclusion
| processing method | Cold Forging | Hot forging |
| Temperature | normal or average or fixed temperature | 900-1,200°C (above recrystallization temperature) |
| feature | High deformation resistance Small dimensional change | Low deformation resistance Large dimensional change and poor accuracy after machining |
| Advantages | High accuracy can be achieved | Capable of processing large items |
| Disadvantages | Molds are prone to wear and tear | Secondary processing is required, which is costly |
| Main Products | Relatively small screws, bolts, nuts, washers, etc. | Relatively large high-pressure valves, pumps, cylinders, etc. |
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

3D Printed Molds for Injection Molding
3D printed molds for injection molding. Learn how this innovative approach enables rapid prototyping, short-run manufacturing, and significant cost savings.
-

Comparison of Silica Sol and Water Glass in Precision Casting
This article will explore the characteristics, applications, and advantages of Silica Sol and Water Glass, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role...
-

Advantages of Nickel Based Alloys in Investment Casting
Investment casting has been an ancient metalworking process,but it has seen modern innovations that make it a highly desirable method for manufacturing precisio...
-
Investment Casting: Unveiling the Magic of Wax Patterns
This guide delves into the various types of investment casting waxes, their unique properties, and how they contribute to the success of this versatile techniqu...
-

From Iron Alloys to Aluminum Alloys: Understanding the World of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals
Delve into the world of metals with this comprehensive guide to ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Explore their properties, applications, and key differences.
-

The Advantages of CNC Machined Parts Over Molded Parts
CNC machining offers numerous advantages over molding. Discover why machined parts are the preferred choice for rapid prototyping and small-batch production in ...

