Casting Defects: Understanding Causes and Solutions
Author: SAIVS Date Published: Sep 18,2024
Casting defects are common issues that occur during the metal casting process. These defects can affect the final product's quality, functionality, and appearance. They often result from issues during the preparation of molds, metal pouring, or cooling. Below is a breakdown of different casting defects, categorized into metallurgical defects, defects due to heat, mold material casting defects, and casting shape defects, along with their causes and possible solutions.
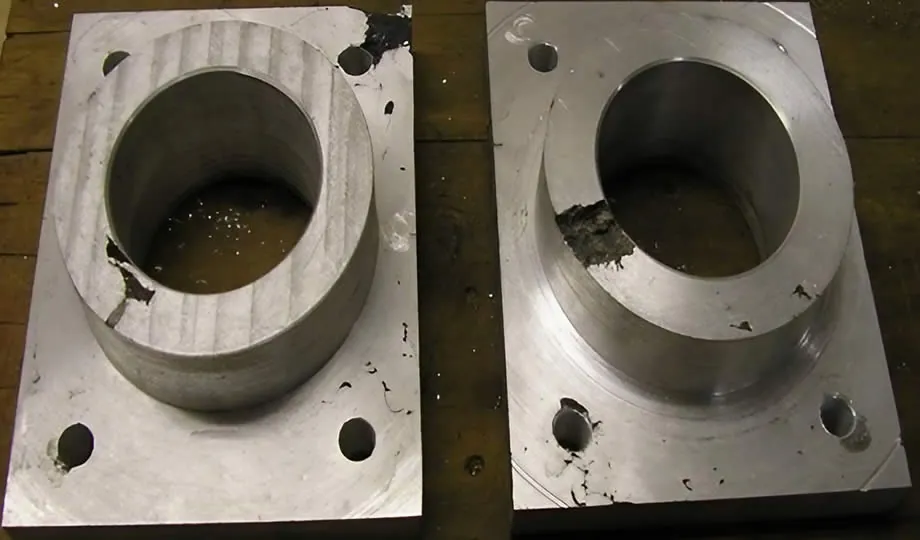
1. Metallurgical Defects
1.1 Porosity Defects
Causes: Porosity refers to small holes or voids in the cast material. These defects occur due to trapped gases in the molten metal or shrinkage during solidification.
Solutions:
Improve mold venting to allow gases to escape.
Use degassing techniques before pouring the metal.
Optimize pouring speed and temperature to reduce gas absorption.
1.2 Sinks
Causes: Sinks are depressions or cavities on the surface of the casting, often caused by uneven cooling and shrinkage.
Solutions:
Properly design the mold to ensure uniform cooling.
Control the pouring temperature and solidification process to avoid shrinkage.
Use chills to promote directional solidification.
1.3 Slag Inclusions
Causes: Slag inclusions occur when non-metallic impurities (slag) are trapped in the casting. They can be introduced during the melting process or from the mold itself.
Solutions:
Properly clean and filter molten metal before pouring.
Improve ladling and pouring practices to avoid slag contamination.
Use fluxes to reduce slag formation during melting.
1.4 Soldering
Causes: Soldering refers to metal sticking to the mold surfaces, making the casting difficult to remove. This happens when the mold or die is too hot or the metal adheres during cooling.
Solutions:
Ensure that mold surfaces are adequately coated with release agents.
Optimize mold temperature to prevent metal adhesion.
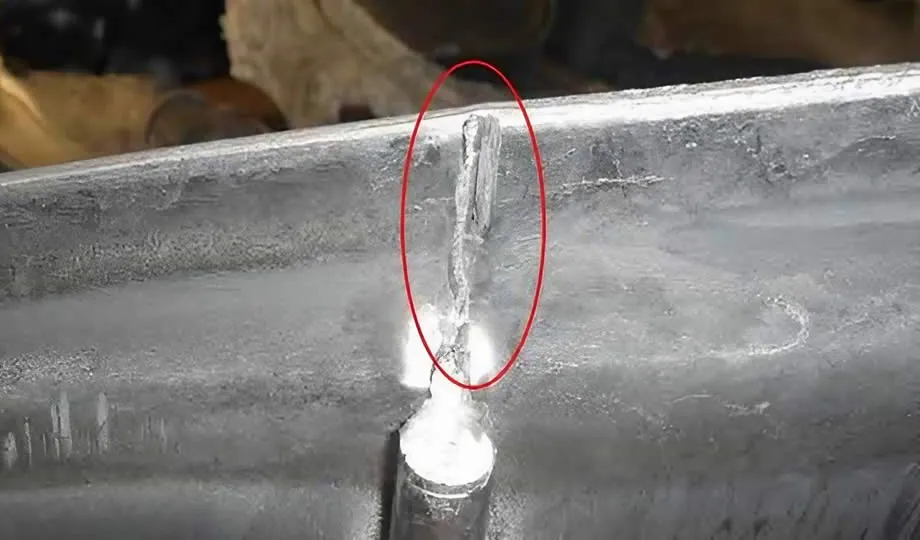

2. Defects Due to Heat
2.1 Hot Tears
Causes: Hot tears are cracks that form during solidification due to internal stresses caused by uneven cooling.
Solutions:
Modify the Mold design to reduce stress concentrations.
Use alloys with better resistance to hot tearing.
Optimize the cooling process to ensure even cooling.
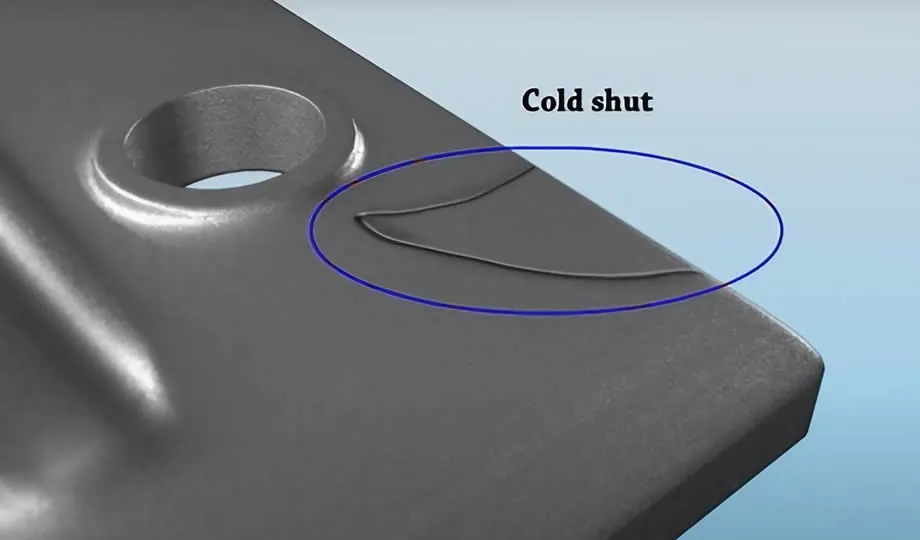
2.2 Cold Shut
Causes: Cold shuts occur when two streams of molten metal do not fuse properly, resulting in weak seams or cracks.
Solutions:
Increase the pouring temperature to ensure better fusion.
Improve mold design to promote smooth metal flow.
Control the pouring speed to avoid premature solidification.
2.3 Thermal Fatigue
Causes: Repeated heating and cooling cycles can cause thermal fatigue, leading to cracks and fractures in the casting.
Solutions:
Use heat-resistant alloys for casting.
Design the casting process to minimize temperature fluctuations.
Properly preheat and cool molds to avoid extreme thermal cycling.
3. Mold Material Casting Defects
3.1 Cuts and Washes
Causes: These defects occur when the molten metal erodes the mold material, resulting in surface imperfections or unwanted material build-up on the casting.
Solutions:
Strengthen mold surfaces to resist erosion.
Control the velocity of molten metal flow to avoid excessive force on the mold.
3.2 Fusion
Causes: Fusion happens when the molten metal fuses with the mold material, causing defects in the surface finish.
Solutions:
Use proper mold materials that resist high temperatures and do not react with the molten metal.
Apply appropriate mold coatings to prevent direct metal contact.
3.3 Runout
Causes: Runout occurs when molten metal leaks out of the mold, resulting in incomplete castings.
Solutions:
Inspect molds thoroughly for any cracks or gaps.
Ensure proper mold assembly and sealing before pouring.
3.4 Swells and Drops
Causes: Swells are unwanted bulges in the casting, while drops occur when loose particles from the mold fall into the molten metal.
Solutions:
Use stronger mold materials to resist deformation under pressure.
Ensure proper handling and preparation of the mold to avoid loose particles.
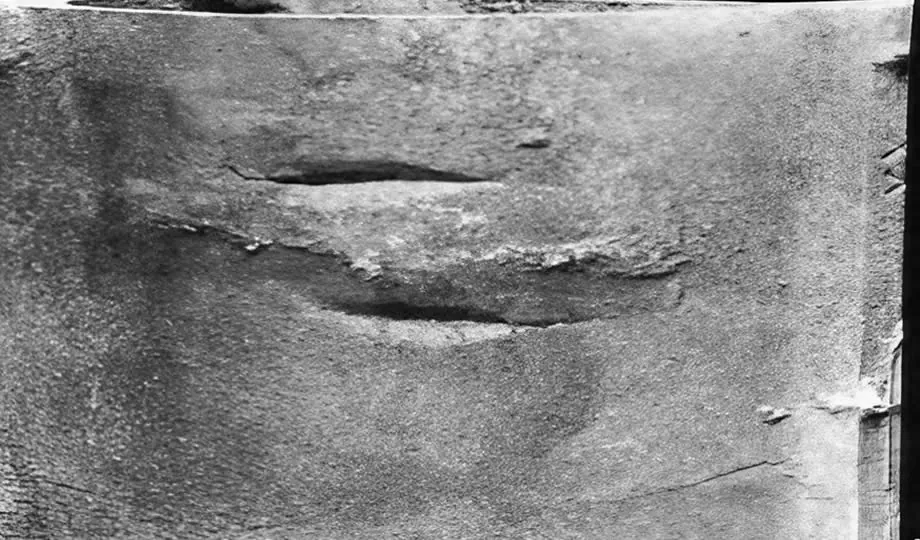

4. Casting Shape Defects
4.1 Mismatches
Causes: Mismatches occur when different parts of the mold do not align properly, leading to casting misalignment.
Solutions:
Carefully align mold parts before pouring.
Ensure the mold is correctly assembled and secured.
4.2 Flash
Causes: Flash is an excess metal that seeps out of the mold, forming a thin, unwanted layer along the parting lines.
Solutions:
Ensure the mold is tightly clamped to prevent metal leakage.
Optimize mold design to minimize parting lines.
Conclusion
Casting defects can significantly impact the quality and functionality of cast products, but understanding their causes can help prevent or reduce their occurrence. By optimizing mold design, controlling the casting process, and using proper materials, manufacturers can reduce defects and improve the overall quality of cast components.
Why Choose SAIVS™ as Your Supplier?
1.Superb Quality Control Management
At SAIVS, we take pride in our perfect quality management systems and procedures, which guarantees the excellent performance of all our producs, being a professional Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingmanufacturer in China.
2.Rich Production Experience
With 20 years of experience in production, SAIVS has a deep understanding of the market and trends, and strives for continuous research and innovation. This has created advantages in both the product's performance and appearance.
3.Competitive Prices
As a Chinese factory committed to becoming the most cost-effective Investment Casting | Die Casting| Sand Castingexporter in China, SAIVS provides high-quality products at advantageous prices. By lowering costs and increasing efficiency, we ensure that our customers receive the best possible value for their investment.
4.Perfect After-sales Service
At SAIVS, we strive to provide superior customer service that meets and exceeds expectations. We are always available for any questions or concerns you may have, and we stand by our commitment to providing excellent after-sales support.
Related Posts
-

Understanding Surface Roughness in CNC Machining
Learn about its importance, measurement, and impact on CNC machined parts, and explore various surface finishes and their applications.
-

How to Maximize the Efficiency of CNC Machining
CNC machining efficiency plays a crucial role in optimizing productivity and reducing costs. Here are some effective ways to improve CNC machining efficien
-

why zinc die casting is used for automotive components
The zinc die casting process is widely used for making components in industrial and building sectors, but the most common application of it is in the automotive...
-

Preventing Flow Lines in Injection Molding
Flow lines, visible as streaks or wave-like patterns on the surface of molded parts, are a common aesthetic defect in injection molding. Although they typi
-

Infiltration, shaping, and repair of die-casting parts
1. Infiltration of die-casting partsInfiltration treatment is the process of immersing a die casting into a infiltration solution with infiltration and filling ...
-

Limitations of CNC Machining
Explore the key limitations of CNC machining. Understand how these factors impact manufacturing efficiency and part quality.

